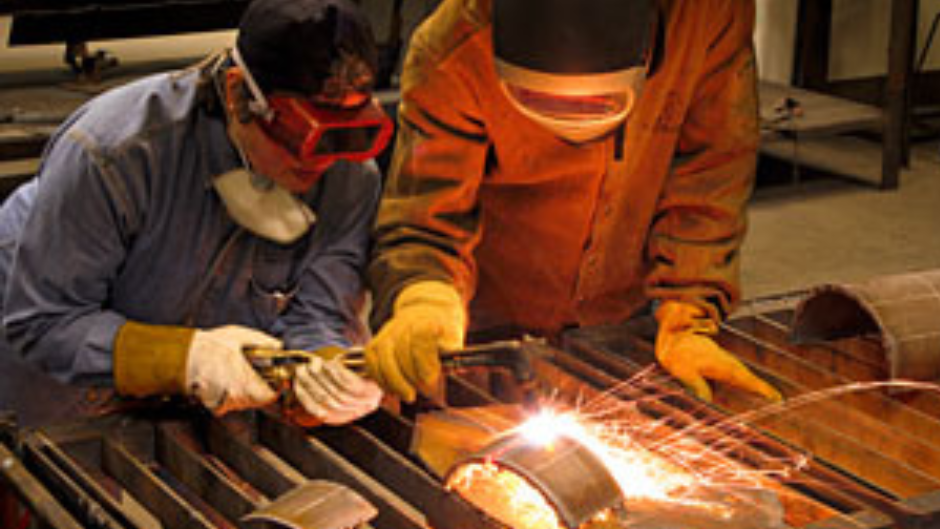
The Welding Technology Program introduces students to both the theoretical and manipulative skills necessary to perform in a broad range of welding careers. Students practice several different types of manual welding and learn the technical and scientific aspects of the welding process.
Processes include SMAW, GMAW, GTAW, FCAW and OAW/OFC
Personal Protective Equipment
All students must have their own Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). See the section on PPE for a full description. If you cannot afford a Helmet, we can loan you a helmet for the laboratory session. Please contact your instructors if you are having difficulty procuring your PPE.
Career Opportunities
Earning a degree in welding technology can open up various career opportunities in the field of welding and metalworking. Welding technology is a specialized field that focuses on joining metals using various welding processes and techniques. Here are some career opportunities you can explore with a welding technology degree:
- Welder/Fabricator: Welders are responsible for joining metal components, structures, and materials using various welding techniques, such as arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, and more. They work in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive.
- Welding Inspector: Welding inspectors are responsible for ensuring that welding work meets quality standards and safety regulations. They inspect welds, perform non-destructive testing, and certify that welding processes are compliant with industry codes and standards.
- Welding Engineer: Welding engineers design welding processes, develop welding procedures, and work on the research and development of new welding technologies. They are involved in improving welding techniques and equipment to enhance efficiency and quality.
- Welding Technician: Welding technicians assist engineers and welders in setting up and maintaining welding equipment. They may also perform inspections, testing, and quality control tasks to ensure welding processes are carried out correctly.
- Robotics Welding Programmer: In manufacturing, welding robots are used to perform welding tasks efficiently. Robotics welding programmers are responsible for programming and maintaining these robotic welding systems, improving their efficiency and accuracy.
- Underwater Welder: Underwater welders are highly specialized professionals who work in underwater welding and construction, typically in the offshore industry. They repair and maintain structures like oil rigs, bridges, and pipelines below the water's surface.
- Welding Instructor/Educator: With additional education and experience, you can become a welding instructor at a technical school or community college. You would teach aspiring welders the skills and knowledge needed for a successful welding career.
- Welding Sales Representative: Sales representatives with expertise in welding technology work for manufacturers and suppliers of welding equipment, consumables, and related products. They help customers select the right welding solutions for their specific needs.
- Welding Business Owner: After gaining experience in the field and acquiring the necessary business skills, you can start your welding business. This may include offering welding services, fabricating metal products, or providing welding equipment and supplies.
- Welding Technician for Aerospace or Defense: The aerospace and defense industries have specific requirements for welding technology. Technicians working in these industries ensure that welds in critical components meet stringent quality and safety standards.
- Pipe Welder: Pipe welders specialize in welding and fabricating pipes for various applications, including pipelines, plumbing, and industrial processes.
- Quality Control Inspector: Quality control inspectors in the welding industry ensure that welding work meets the specified standards and is safe for its intended use.
It's important to note that career opportunities and advancement may vary depending on your location, experience, and the specific welding processes and materials you specialize in. Continuing education and certifications in welding can also enhance your career prospects and earning potential in this field.
Required PPE
- Helmet: all course, except weld 221 A-B
- Gas welding goggles: Weld 205 and 221 A-B
- Welding Gloves: required for all courses, specific types for each course
-
- Weld 203, GTAW: TIG gloves
- Weld 205 Introduction to Welding: medium weight MIG gloves
- Weld 204, GMAW: MIG gloves
- Weld 211, SMAW: MIG gloves or heavy weight gloves
- Weld 221 OAW: medium weight MIG gloves
-
- Safety glasses: polycarbonate, ANSI 87.1,
- Ear plugs: washable silicone with lanyard
- Breathing protection: Half mask Respirator with p100 or N95 mask, required under COVID.
- Welding Jacket: preferred either Fire Retardant (FR) cotton or leather welding jacket
- Welding cap for head: all cotton
- Long Pants: cotton/denim
- Closed Toe Leather Shoes: preferred either work boots or steel toe